Abstract
Introduction: Early-onset myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) in adults (16-60 yo) accounts for 5-10% of all MDS cases. WHO 2022 Myeloid neoplasms with germline predisposition without a pre-existing platelet disorder or organ dysfunction only includes 2 genes in this subset of patients: DDX41 and TP53. We aim to depict this subset-germline variant landscape in a spanish multicenter cohort of patients with data from paired tumor-germinal exome sequencing, searching for recurrently mutated genes.
Methods: Prospective cohort study (2014-2022) of 205 patients from 30 Spanish Group of Myelodysplastic Syndrome (GESMD) centers with a de novo diagnosis of MDS between 16-60 years old, without prior organ dysfunction or thrombopenia. Therapy-related cases were excluded. We gathered data from 107 clinical variables in relation to family and personal history, diagnosis, treatment, HSCT and disease evolution. Whole exome sequencing was performed in paired tumor-germline samples on NovaSeq6000-Illumina platform (average depth 100x, 150 million reads per sample and quality Q30a>95%). Analysis of variants by a homemade pipeline: eliminating intronic, synonymous and those with frequency in the population>1%. The germline variants were categorized according to ACMG criteria.
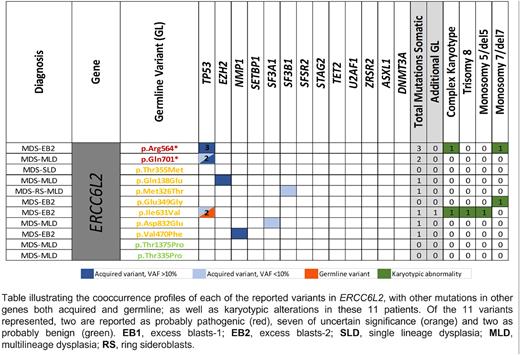
Results: In the global cohort of 205 cases of adults diagnosed with MDS with an early onset (median age at diagnosis, 49 years, range 38-55), we found 11 patients carrying germline variants in ERCC6L2, as the most recurrently affected gene in the DNA Repair system. Nine of the 11 cases were heterozygous. Within the ERCC6L2 cases, the mean age at onset was 44 yo (range 16-55) The 11 variants were likely-pathogenic (LP, n=2), of uncertain significance (VUS, n=7) and probably benign (n=2) (Figure 1). However, carriers of the germline variants in ERCC6L2 had a significantly higher frequency of monosomy 7 and acquired mutations in TP53, mostly, multihit (p=0.04 and p=0.02, respectively). We highlight that two carriers of germline variants, one of them in heterozygosis (p.Glu349Gly; VUS) and another in homozygosis (p.Arg564*; LP), acquired a monosomy of chromosome 7. Three patients presented concurrent acquired mutations in TP53, in one of the cases the germline variant in ERCC6L2 was also interpreted as VUS and presented in heterozygosis. The presence of a germinal variants in LP/VUS ERCC6L2 showed prognostic independence (p=0.006, HR 4.468) compared with the dichotomized IPSS-R (<3.5 or >3.5), when considering overall survival as endpoint event. In addition, the frequency of patients with germline variants (VUS+LP+P) according to the gene function or pathway were 38.1% in DNA damage response, 2% telomere function maintenance, 9.6% hematopoiesis regulators, 6.1% ribosome function, 14.7% immune response, 13.3% chromatin modifiers, 14.2% cell cycle and proliferation, 12.7% platelet function, 7.1% erythroid synthesis and 22.8% signaling activation.
Conclusion: We describe that variants in ERCC6L2 are associated with MDS onset in adults, without previous organ dysfunction or thrombocytopenia. These carriers show: i) frequent heterozygous configuration, ii) acquired lesions similar to those described in biallelic predisposition in children in one third of the cases and iii) an unfavorable clinical impact.
Disclosures
Diez-Campelo:Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BluePrint: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Jerez:BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal